Certificate MMC access
- Run the MMC either from the start menu or via the run tool accessible fom the WIN+R shortcut.
- Click on File - Add/Remove Snap-in.
- Select Certificates in the left panel and click on Add.
- In the new window, click on Computer Account.
- Select Local Computer then click on Finish.
- Complete the adding dialog by clicking OK.
Request generation
- In the certificate management console, select in the folder tree Certificates - Personal- Certificates. In the certificate list, in the central panel, right click then select All Tasks - Advanced Operations - Create Custom Request.
- In the new windows, select Proceed without enrollment policy under Custom Request then click Next.
- Select (No Template) CNG Key as the template and PKCS #10 as the request format. Then, click Next.
- Develop the details by clicking the arrow and click on Properties.
- In the properties window, in the tab General, enter a Friendly Name that will be displayed in your certificate management interfaces and optionally, a description.
- In the Subject tab, in the Subject Name box, add the attributes to be added to the certificate, then click on Add to add them to the request.
- A standard certificate will generally contain the CN, O, L, ST, and C fields.
- In the Private Key tab, you can choose the CSP, the key formats, and its options.
- For a RSA key, we recommend a key size of 2048bits. We also reocomment the SHA256 hash algorithm for the CSR signature.
- You can also generate ECC keys using this tool. Attention, you will need to sign your CSR using SHA256.
- Once the properties dialog has been completed, you can resume the CSR generation and finish the request after having chosen a file name and directory. It is important to choose the Base 64 format.
Create a SAN CSR using MMC
If you want to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for a Subject Alternative Names (SAN) certificate, you can use the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) to create such a request.
On a Windows computer open MMC.exe and add the Certificates snap-in.
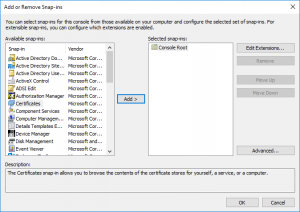
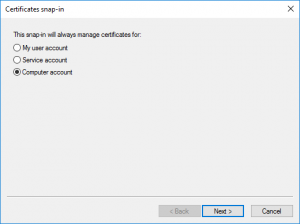
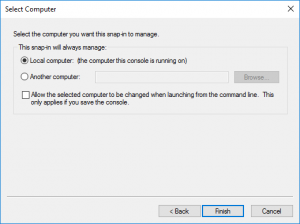
Make sure you choose ‘Computer account’ to manage certificates for on the local computer.
Rightclick on the Certificates folder and choose ‘All Tasks’ –> ‘Advanced Operations’ –> ‘ Create Custom Request’.
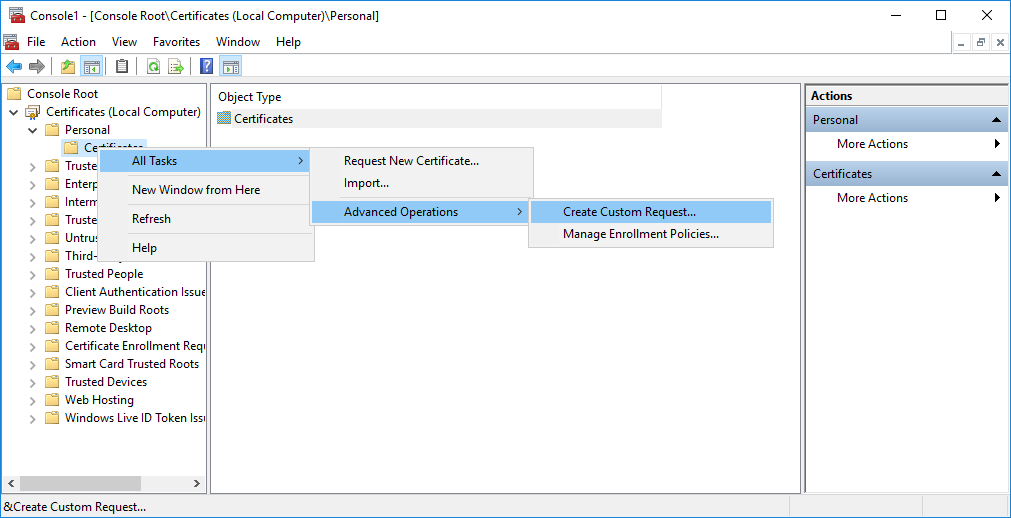
Click Next on the informational screen.
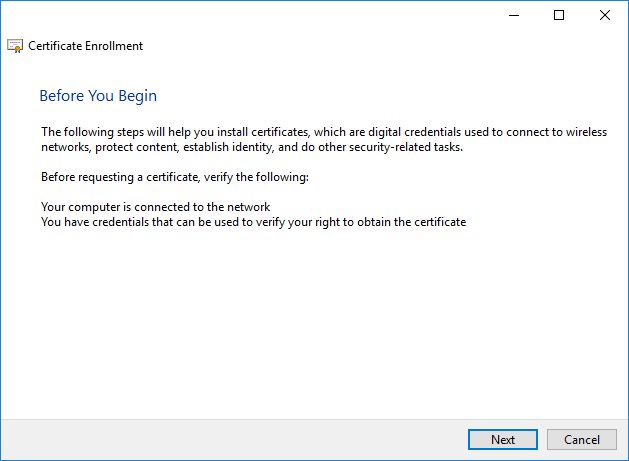
Choose ‘Proceed without enrollment policy’ and click Next.
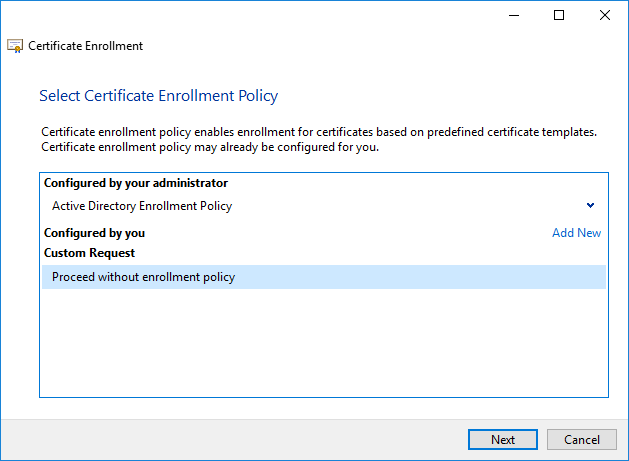
Change the Template to ‘(No template) Legacy key’ for compatibility and click Next.
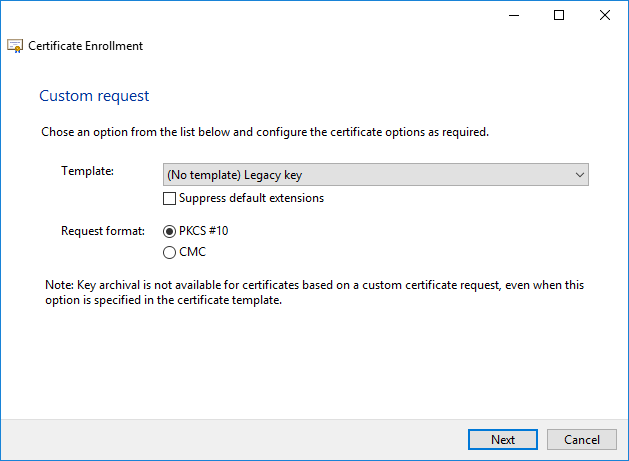
Click on the Properties button to configure the CSR.
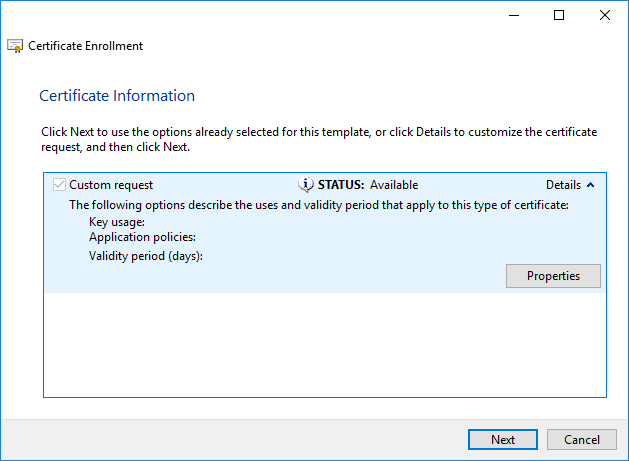
Enter a Friendly name and a description. This is only used to identify the certificate easily. Click Apply when ready and go to the Subject tab.

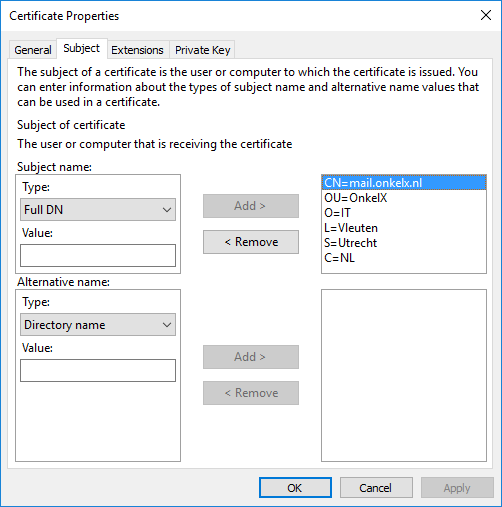
At the Subject name section, leave the type to Full DN. Use the Value field to enter administrative information.
Example:
CN=mail.onkelx.nl
OU=OnkelX
O=IT
L= Vleuten
S=Utrecht
C=NL
Put each of these values in the Value field and click Add to add the value.
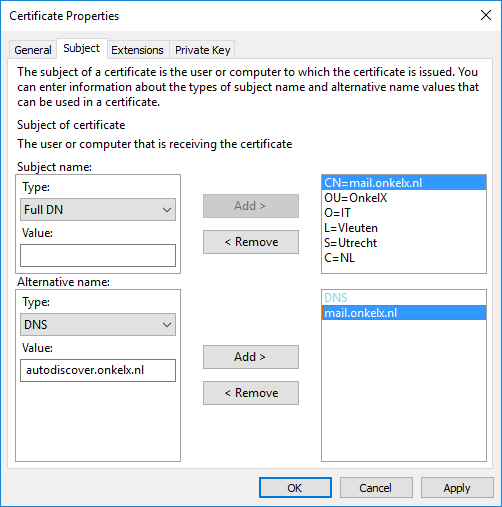
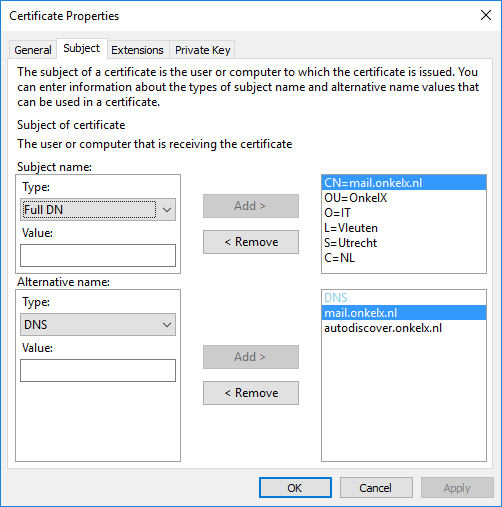
In the Alternative name section, add all DNS names that you want as alternative names. Also include the common name that you already added in the Subject name section. This is required because if an SSL certificate has a Subject Alternative Name (SAN), then SSL clients are supposed to ignore the Common Name value and seek a match in the SAN list. Click Apply when ready and go to the Extensions tab.
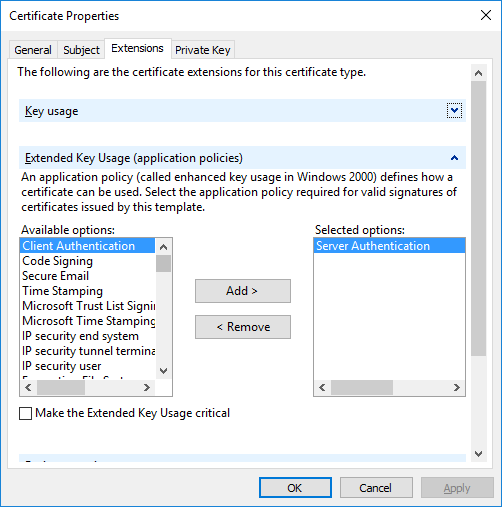
Open the Extended Key Usage (application policies) section, and add ‘Server Authentication’ to the Selected options.
Click Apply and go to the Private Key tab.
Open the Key options section and set the Key size to at least 2048. If you need to export the certificate including the private key, enable the ‘Make private key exportable’ option. When ready, click Apply and OK.

All CSR information has been added now. Click Next to proceed.
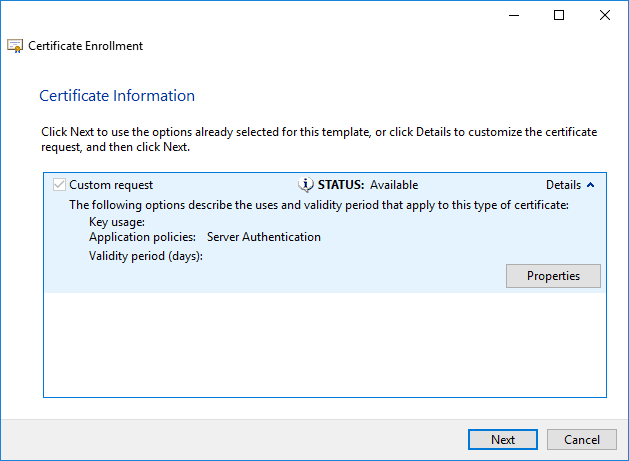
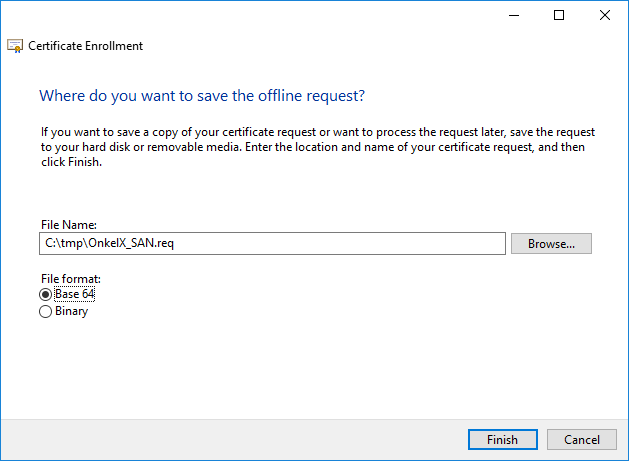
Specify a file name and location for the CSR and leave the File format to Base 64. Click Finish to save the file.
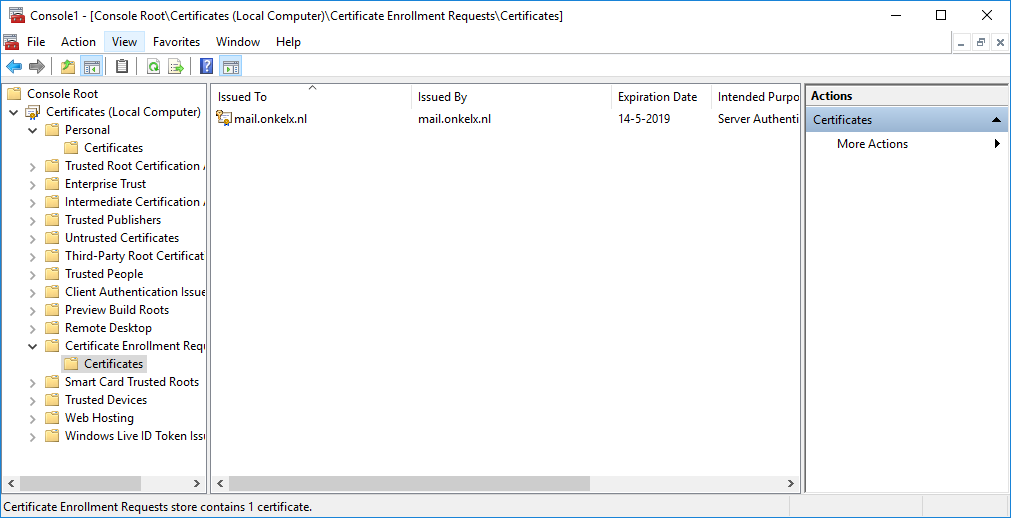
When you look at the Certificate Enrollment Requests in the MMC, you will see the CSR. This will automatically be removed once you import the certificate.
To verify your CSR, you can use a CSR checker on the Internet.
https://www.digicert.com/ssltools/view-csr/
Open your CSR file, copy the content to the webpage and click the ‘Check CSR’ button.
Check if all values are correct.
Now you can use the CSR to request an SSL SAN certificate. You can use your own (Microsoft) CA, or a commercial CA.















